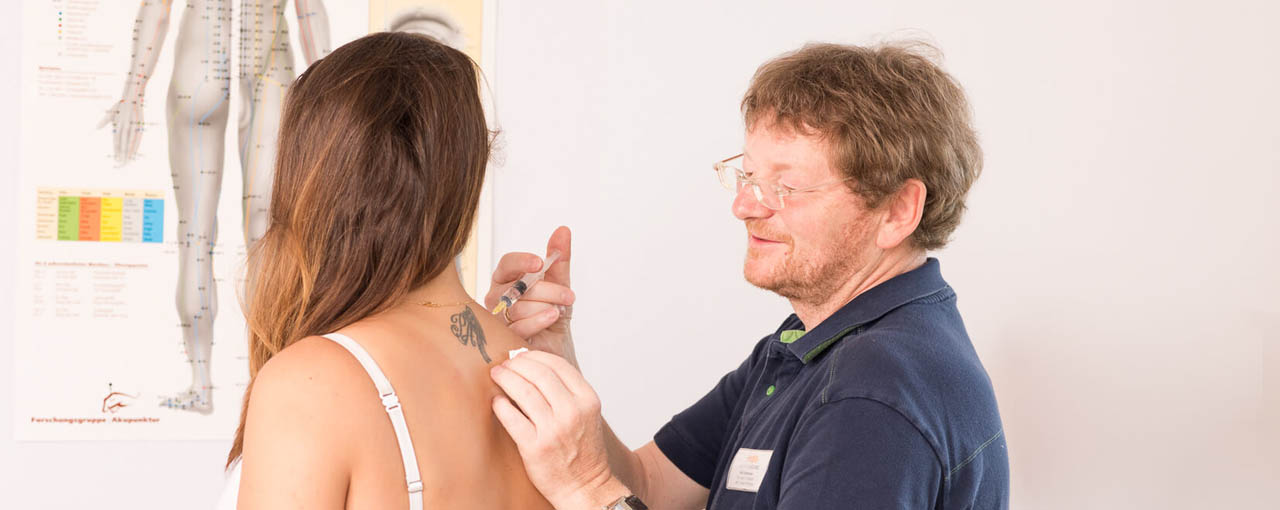
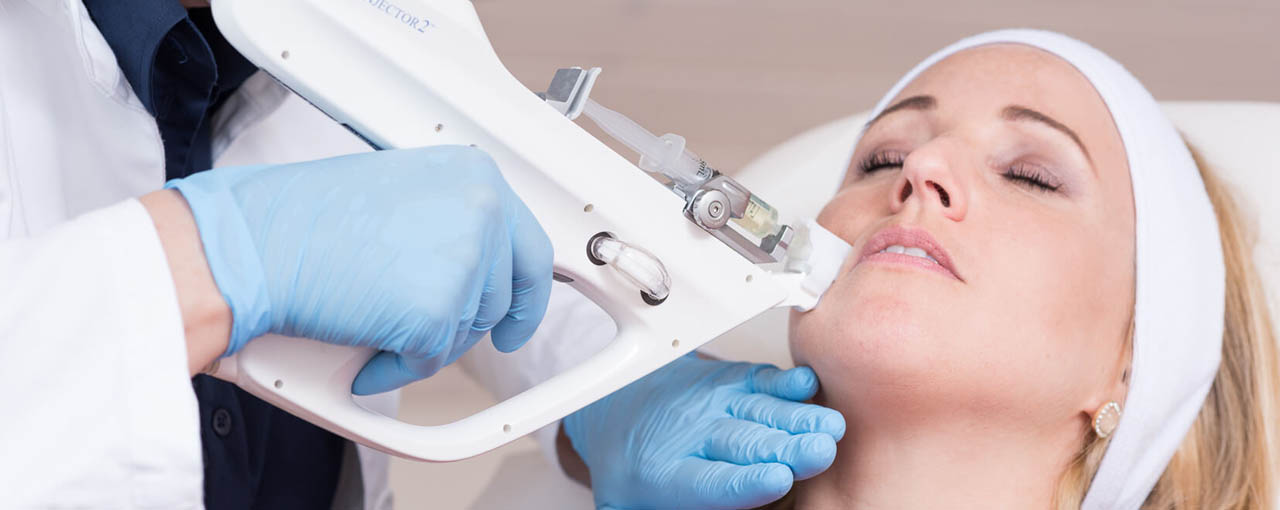
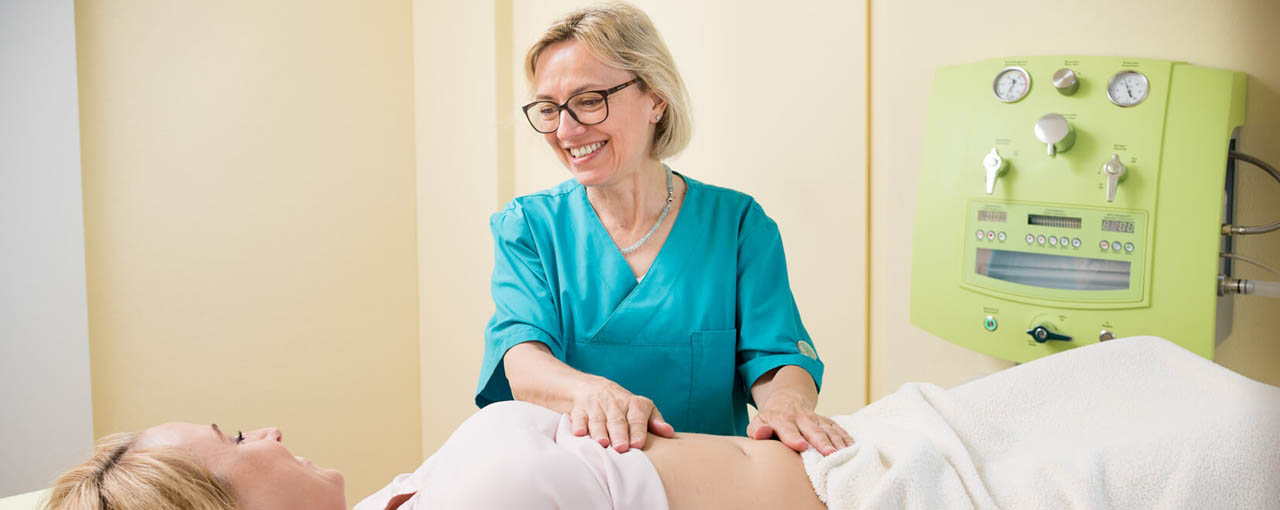
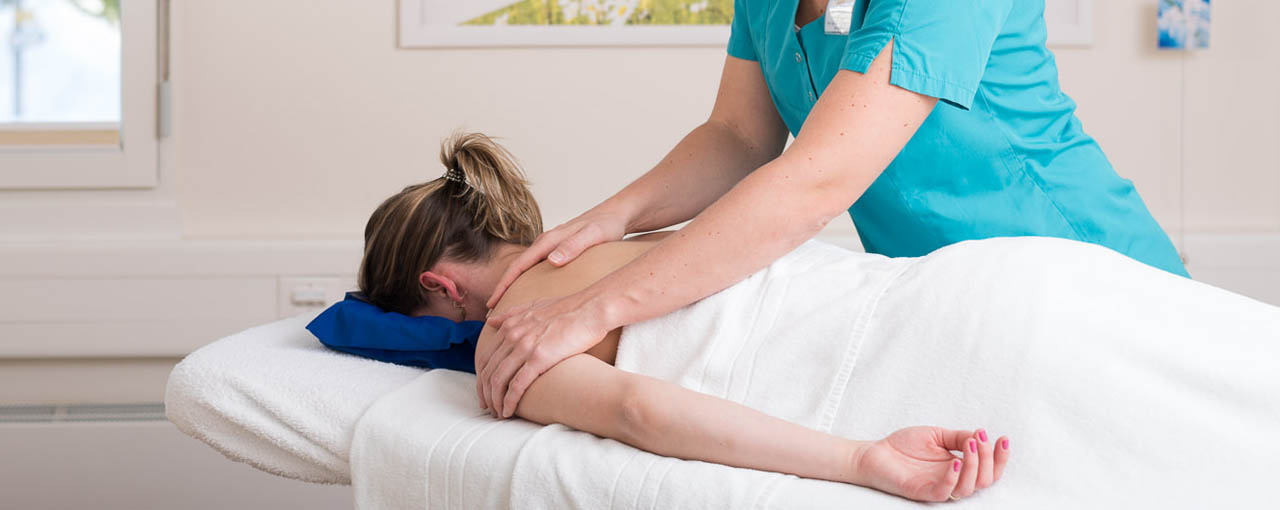
What you can expect from us
Our therapy concept
We look at the person as a whole and bring together a variety of complementary medical diagnostic and therapeutic methods, regardless of whether the treatment is relatively simple or the patient suffers from profound chronic symptoms. Dentistry also plays an important role in the treatment of physical disorders. Through energy channels in our body, the so-called meridians, the teeth are connected to the body’s organs. Therefore, the causes of physical complaints can often be found in the teeth.
For us, holistic medicine means that we not only look at the body, but also involve your living environment, together with you. Environmental burdens, mental pressure or stress can increase symptoms. If environmental burdens are reduced, or even eliminated, this has a positive effect on the healing success. As a rule, we use a four-stage approach in our clinic:
The four-stage concept
1.
Cause Analysis
Details
2.
Release & relief
Details
3.
Regeneration & biostimulation
Details
4.
Harmonization & awareness
Details
Top-level integrative whole-body medicine
Our therapies in the overview
As physicians and dentists originally trained in conventional medicine, we have acquired knowledge from various alternative forms of therapy over the years. Our greatest strength is the successful bringing together of the various disciplines of complementary medicine, such as homeopathy and acupuncture.
Through the interaction of the individual disciplines, we achieve results that would otherwise never have been possible. Below we will discuss the most important holistic therapies that we apply daily in our clinic.
Human Medicine
Dentistry
Specialized in sensitive patients with acute, chronic, and unidentified illnesses
Our main focus on indications
Orthodontics
read more
Dental hygiene
read more
General for all chronic diseases and cancer
Full body check-up to evaluate the main causative factors
Autoimmune Diseases
Rheumatoid polyarthritis and juvenile arthritis
Bechterew´s disease = Spondylitis ancylosans
Crohn’s disease (autoimmune ileo-colitis)
Hashimoto’s thyroiditis and Basedow’s disease
Myelodystrophic syndrome
ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis)
Ulcerative colitis
Sjögren’s syndrome
Lupus erythematodus
Idiopathic thrombopenia
Inclusion body myositis
Chronic Infections
Borreliosis (also known as Lyme’s disease)
Chronic susceptibility to infection
Chronic virus infestation (EBV, CMV, coxsackievirus, herpes, hepatitis)
Chronic parasite infestation (toxoplasmosis, malaria, pinworms, liver flukes, etc.)
Chronic bacterial infections (sinusitis, tonsillitis, appendicitis, osteomyelitis, etc.)
Chronic fungal infections like dermatophyte, nail fungus or vaginal mycosis
Specific infections caused by Bartonella, Shigella, salmonellae or Yersinia
Chlamydia infections
Mycoplasma infections
Neurological Diseases
Parkinson´s disease
Alzheimer´s disease
Guillain-Barré syndrome
Post-zoster neuralgia
Psycho-vegetative disbalance
Multiple Sclerosis
Polyneuropathy
Myopathy
Encephalopathies
Moto neuron disease
Joint, Back and Bone Disorders
Gon- and coxarthrosis
Post-arthritic arthrosis (pcP, Bechterev , psoriatic arthritis)
Degeneration of the intervertebral disks
Osteopenia (osteoporosis, osteomalacia)
Tendopathy (e.g. rotator cuff problems)
Poly-arthrosis (Heberden’s , Bouchard’s)
Spondylosis, spondyl-arthritis
Paget’s disease
Enthesitis (e.g. archer’s elbow)
Chronic backache and joint pain
Paediatrics
Hyperkinetic syndrome (ADHD) and autism
Lack of concentration and behavioural problems
Weight problems in childhood and adolescents
Allergies/intolerances
Diabetes type I (no first diagnosis, no first treatment)
Endogenous eczema
Inexplicable pain
HPU/KPU in childhood
Juvenile rheumatoid diseases
Constipation/diarrhea in childhood
Women’s health
Bioidentical hormones
Menopausal symptoms
Libido loss
Infertility
Dysmenorrhea
Cycle irregularities
Digestive Disorders
Celiac disease
Ulcerative colitis
Chronic constipation
Food allergies and intolerances
Haemorrhoids
Irritable bowel syndrome
Crohn´s disease
Heartburn
Helicobacter infections
Chronic diarrhea
Peptic esophagitis
Chronic abdominal pain
Metabolic Diseases
Diabetes mellitus
Anorexia
Adrenal disorders
Hyper- and hypothyreosis
Hyperuricemia (gout)
Hyperhomocysteinemia
Obesity
Pituitary disorders
Kryptopyrrol-urea/KPU/HPU
Chronic pancreatopathy
Metabolic syndrome
High cholesterol (hypercholesteremia)
Cardio-vascular Diseases
Post-coronary conditions
Venous disorders (varicosis, phlebitis, venous leg ulcers)
Coronary heart disease (CHD)
Post-cerebral infarct conditions and conditions after transitory cerebral hypoperfusion
Inflammatory and degenerative blood vessel disorders (arteriosclerosis, atheromatosis, arteriitis, vasculitis)
Hypotension and hypertension
Lymphedema (primary and secondary)
Angina pectoris
Respiratory, pulmonary and dermatological Diseases
Hay fever (pollinosis)
Eczema
Asthma bronchiale
Neurodermatitis
Loss of hair
Sarcoidosis
Contemporary Diseases
Chronic fatigue
All kinds of chronic pain, migraines and headaches
Dysthymia, anxiety and depression
Psychosomatic disorders
Menstrual disorders, dysmenorrhea
Hyper-sensitivity to environmental conditions (electric and magnetic fields, high-frequency fields, chemical substances)
Fibromyalgia
Burnout
Attention deficit disorder (ADD)
Endocrine disorders
Somatization disorders
Cancer, early Stages and integrative to classic Oncology
Early stages of cancer and Lymphoma can be fully managed, for example
Prostate cancer and breast cancer in stages 1 and 2
Pre-canceroses, such as lichen ruber planus, leukoplakia
All types of cancer (carcinoma) without metastases
Advanced cancer stages (with metastasis) needs to be evaluated on individual basis according to needs and possibilities
Carcinoma in situ (e.g. on the breast)
Most skin cancers
Cervical dysplasia (Papanicolau 2-4)
Lymphoma and chronic Leukaemia
Lymphomas (Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin)
Myelomatosis
Myelodysplastic Syndrome
Thrombocytosis
Primary myelopathic polycythemia and of course, as previously mentioned
Plasmocytoma
Kahler’s disease
Myelofibrosis
Chronic leukemia
Aspects of Dentistry as part of Whole Body Dentistry
Dental Hygiene
Filling materials and therapies (temporary, long term, defect-oriented management of decay)
Direct, indirect dental restorations (ceramic)
Tooth fragments, foreign bodies, dead teeth
Bone infections of the jaw (jaw cavitation, jaw ostitis)
Oral lesions due to bacterial, viral, parasitic overload (compromised immune system) up to precancerous conditions
Bite rehabilitation according to physiological rules (fixed vs. removable solutions according to health condition of patient, e.g. dentures vs. crowns/bridges vs. implants)
Gingivitis, Periodontitis
Impacted & displaced teeth
Craniomandibular Dysfunction
Bite correction/orthodontics
Do you have questions?